Page 29 - PDF_Flip_Book
P. 29
Chapter 9 - Airspace: The Wild Blue, Green & Red Yonder 9-41
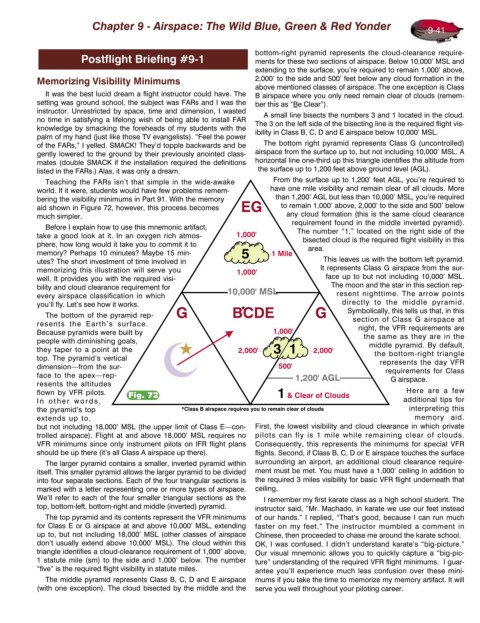
bottom-right pyramid represents the cloud-clearance require-
Postflight Briefing #9-1 ments for these two sections of airspace. Below 10,000’ MSL and
extending to the surface, you’re required to remain 1,000’ above,
Memorizing Visibility Minimums 2,000’ to the side and 500’ feet below any cloud formation in the
above mentioned classes of airspace. The one exception is Class
It was the best lucid dream a flight instructor could have. The B airspace where you only need remain clear of clouds (remem-
setting was ground school, the subject was FARs and I was the ber this as “Be Clear”).
instructor. Unrestricted by space, time and dimension, I wasted
A small line bisects the numbers 3 and 1 located in the cloud.
no time in satisfying a lifelong wish of being able to install FAR The 3 on the left side of the bisecting line is the required flight vis-
knowledge by smacking the foreheads of my students with the ibility in Class B, C, D and E airspace below 10,000’ MSL.
palm of my hand (just like those TV evangelists). “Feel the power
of the FARs,” I yelled. SMACK! They’d topple backwards and be The bottom right pyramid represents Class G (uncontrolled)
gently lowered to the ground by their previously anointed class- airspace from the surface up to, but not including 10,000’ MSL. A
mates (double SMACK if the installation required the definitions horizontal line one-third up this triangle identifies the altitude from
listed in the FARs.) Alas, it was only a dream. the surface up to 1,200 feet above ground level (AGL).
Teaching the FARs isn’t that simple in the wide-awake From the surface up to 1,200’ feet AGL, you’re required to
world. If it were, students would have few problems remem- have one mile visibility and remain clear of all clouds. More
bering the visibility minimums in Part 91. With the memory than 1,200’ AGL but less than 10,000’ MSL, you’re required
aid shown in Figure 72, however, this process becomes to remain 1,000’ above, 2,000’ to the side and 500’ below
much simpler. any cloud formation (this is the same cloud clearance
requirement found in the middle inverted pyramid).
Before I explain how to use this mnemonic artifact,
The number “1,” located on the right side of the
take a good look at it. In an oxygen rich atmos- bisected cloud is the required flight visibility in this
phere, how long would it take you to commit it to area.
memory? Perhaps 10 minutes? Maybe 15 min-
utes? The short investment of time involved in This leaves us with the bottom left pyramid.
memorizing this illustration will serve you It represents Class G airspace from the sur-
well. It provides you with the required visi- face up to but not including 10,000’ MSL.
bility and cloud clearance requirement for The moon and the star in this section rep-
every airspace classification in which resent nighttime. The arrow points
you’ll fly. Let’s see how it works. directly to the middle pyramid.
Symbolically, this tells us that, in this
The bottom of the pyramid rep-
section of Class G airspace at
resents the Earth’s surface. night, the VFR requirements are
Because pyramids were built by the same as they are in the
people with diminishing goals, middle pyramid. By default,
they taper to a point at the
the bottom-right triangle
top. The pyramid’s vertical
represents the day VFR
dimension—from the sur- requirements for Class
face to the apex—rep- G airspace.
resents the altitudes
flown by VFR pilots. Here are a few
Fig. 72
In other words, additional tips for
the pyramid’s top interpreting this
extends up to, memory aid.
but not including 18,000’ MSL (the upper limit of Class E—con- First, the lowest visibility and cloud clearance in which private
trolled airspace). Flight at and above 18,000’ MSL requires no pilots can fly is 1 mile while remaining clear of clouds.
VFR minimums since only instrument pilots on IFR flight plans Consequently, this represents the minimums for special VFR
should be up there (it’s all Class A airspace up there). flights. Second, if Class B, C, D or E airspace touches the surface
The larger pyramid contains a smaller, inverted pyramid within surrounding an airport, an additional cloud clearance require-
itself. This smaller pyramid allows the larger pyramid to be divided ment must be met. You must have a 1,000’ ceiling in addition to
into four separate sections. Each of the four triangular sections is the required 3 miles visibility for basic VFR flight underneath that
marked with a letter representing one or more types of airspace. ceiling.
We’ll refer to each of the four smaller triangular sections as the I remember my first karate class as a high school student. The
top, bottom-left, bottom-right and middle (inverted) pyramid. instructor said, “Mr. Machado, in karate we use our feet instead
The top pyramid and its contents represent the VFR minimums of our hands.” I replied, “That’s good, because I can run much
for Class E or G airspace at and above 10,000’ MSL, extending faster on my feet.” The instructor mumbled a comment in
up to, but not including 18,000’ MSL (other classes of airspace Chinese, then proceeded to chase me around the karate school.
don’t usually extend above 10,000’ MSL). The cloud within this OK, I was confused. I didn’t understand karate’s “big-picture.”
triangle identifies a cloud-clearance requirement of 1,000’ above, Our visual mnemonic allows you to quickly capture a “big-pic-
1 statute mile (sm) to the side and 1,000’ below. The number ture” understanding of the required VFR flight minimums. I guar-
“five” is the required flight visibility in statute miles. antee you’ll experience much less confusion over these mini-
The middle pyramid represents Class B, C, D and E airspace mums if you take the time to memorize my memory artifact. It will
(with one exception). The cloud bisected by the middle and the serve you well throughout your piloting career.